Customer journey mapping in market research: A data-driven approach
Discover how market research makes customer journey mapping more accurate, helping businesses uncover insights and improve experiences.

Every business wants to understand its customers better. But here’s the thing—customer behavior isn’t linear. People don’t just see an ad, click “buy,” and call it a day. They browse, compare, hesitate, get distracted, return later, and interact with multiple touchpoints before making a decision. This is where Customer Journey Mapping (CJM) comes in.
A Customer Journey Map is a visual representation of a customer’s experience with a brand across different stages and touchpoints. It highlights key moments, pain points, and opportunities for improvement.
For market researchers, CJM isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s a data-backed framework to decode customer behavior. It helps businesses understand:
✔ What drives customer decisions
✔ Where they drop off
✔ How they interact with different channels
✔ What influences loyalty and retention
Unlike simple surveys or isolated user feedback, CJM connects the dots between qualitative and quantitative insights. By integrating real-world data, businesses can create journeys that are not just mapped but optimized for better customer experiences.
In this blog, we’ll break down:
✅ How market research fuels CJM
✅ Key components of a customer journey map
✅ How to build an actionable CJM backed by data
✅ Common mistakes and best practices
✅ Real-world applications of CJM in market research
Let’s get started 🚀
The role of market research in customer journey mapping
Customer Journey Mapping (CJM) isn’t just about sketching out an ideal customer path—it’s about grounding those insights in real data. This is where market research plays a crucial role. Without research, journey maps are based on assumptions, which can lead to misaligned strategies, wasted resources, and poor customer experiences.
1. Gathering qualitative and quantitative data
A strong journey map relies on a mix of qualitative and quantitative research:
- Quantitative research helps identify broad trends and patterns in customer behavior. This includes website analytics, heatmaps, survey responses, click-through rates, and conversion data. These numbers reveal what’s happening at each stage of the journey.
- Qualitative research adds depth by explaining the why behind customer actions. This includes in-depth interviews, focus groups, customer support logs, and open-ended survey questions that uncover emotions, motivations, and pain points.
Together, these data sources provide a holistic view of the customer journey—going beyond surface-level interactions to understand intent, friction points, and unmet needs.
2. Identifying customer touchpoints and pain points
A customer doesn’t interact with a business through a single channel. They might:
📌 Click on an ad
📌 Visit a website
📌 Compare reviews on third-party platforms
📌 Engage with customer support
📌 Abandon a cart, only to return days later
Market research helps businesses identify every key touchpoint in the journey and pinpoint where things go wrong. Heatmaps, session recordings, NPS (Net Promoter Score) surveys, and interview feedback can reveal where customers experience friction—be it a confusing checkout process, lack of information, or poor customer service.
3. Utilizing surveys, interviews, and focus groups
Market researchers use a variety of methods to validate and refine customer journey maps:
✔ Surveys: Short, targeted questionnaires can measure customer satisfaction at different touchpoints (e.g., post-purchase, after customer support interactions).
✔ Interviews: One-on-one discussions uncover deeper emotions and motivations behind decision-making.
✔ Focus groups: Group discussions highlight common themes in customer behavior and identify shared frustrations or expectations.
✔ User testing: Watching real users navigate a website or app uncovers usability issues that wouldn’t show up in raw analytics.
By combining data-driven insights with real customer voices, market research turns CJM from a static exercise into a powerful optimization tool.Customer Journey Mapping without market research is like navigating a city with an outdated map—you might reach your destination, but you’ll hit roadblocks along the way. Good market research ensures your journey maps reflect reality, not assumptions.
Key components of a customer journey map
A customer journey map is not just a flowchart of customer interactions. It is a detailed, data-driven framework that captures what a customer thinks, feels, and experiences at each stage. Understanding its key components ensures that the journey map is actionable and aligned with real customer behavior.
Customer personas
A journey map is only useful if it reflects real customer experiences, which is why it starts with customer personas. These are detailed profiles of your ideal customers based on demographics, behaviors, motivations, and pain points.Market research helps create accurate personas by gathering data from customer surveys, interviews, and behavioral analytics. Instead of making broad assumptions, personas should be built using real customer insights to reflect different customer types who interact with your business.For example, an enterprise SaaS company might have one persona representing small business owners looking for cost-effective solutions and another representing corporate decision-makers prioritizing scalability and integrations. Each will have different journeys, expectations, and challenges.
Stages of the customer journey
The customer journey is divided into key stages, each representing a step in the decision-making process. While the stages can vary based on industry, they typically follow a structure like this:
- Awareness – The customer realizes a need or problem and starts looking for solutions.
- Consideration – They compare different options, research alternatives, and evaluate features.
- Decision – They make a purchase or commit to a service.
- Retention – The post-purchase experience determines if they will return or recommend the brand.
- Advocacy – If the experience is positive, the customer may become a brand advocate and refer others.
Market research helps define what happens at each stage and what factors influence movement between them. Surveys and data analytics can reveal where drop-offs occur, helping businesses address friction points before they lead to churn.
Customer goals and expectations at each stage
At every stage, customers have specific goals and expectations. Understanding these helps businesses tailor messaging, content, and services to meet those needs.For instance, during the awareness stage, a customer may simply want informative content that educates them about a problem. By the consideration stage, they may expect detailed comparisons and customer testimonials to validate their choice.Market researchers use sentiment analysis, social listening, and behavioral tracking to identify what customers expect at different points in their journey. Addressing those expectations makes the journey smoother and more engaging.
Touchpoints and channels
A touchpoint is any interaction between a customer and a brand—whether digital or offline. Common touchpoints include:
- Website visits – Landing pages, product pages, blog content
- Ads and social media – Sponsored content, organic posts, influencer marketing
- Customer support – Live chat, email, call centers
- Reviews and referrals – Third-party platforms, testimonials, word-of-mouth
- Post-purchase interactions – Order confirmation, onboarding emails, loyalty programs
Different personas may prefer different touchpoints, which is why market research is critical in mapping how customers engage with a brand. Identifying which channels drive the most engagement, satisfaction, or frustration can help businesses prioritize improvements where they matter most.
Emotional responses and pain points
A journey map is incomplete without understanding how customers feel at each stage. A well-mapped journey includes emotions tied to each touchpoint—from excitement to frustration.Pain points, or obstacles that disrupt the experience, are often why customers abandon a journey. These could be:
- Confusing website navigation
- Lack of product information
- Long response times from customer support
- Unexpected costs at checkout
Market researchers conduct in-depth interviews, usability tests, and customer satisfaction surveys to capture these emotions and pinpoint where frustration peaks. Addressing these weak spots ensures a more seamless, friction-free experience.
Steps to create an effective customer journey map
Creating a customer journey map isn’t just about sketching out steps—it’s about backing every stage with real customer insights to ensure it reflects actual behaviors, challenges, and expectations. Market researchers play a crucial role in making this process data-driven and actionable. Here’s how to do it step by step.
1. Define clear objectives for the CJM initiative
Before creating a journey map, it’s essential to define why you’re doing it and what you want to achieve. Different businesses use CJM for different reasons, such as:
- Identifying bottlenecks in the conversion process
- Understanding why customers drop off at certain stages
- Improving customer retention and loyalty
- Optimizing marketing, sales, or product experiences
Market research ensures that these objectives align with real customer needs rather than internal assumptions. Conducting stakeholder interviews and customer surveys can help clarify which pain points need solving first.
2. Conduct thorough customer research
Market research lays the foundation for an accurate, insight-driven journey map. The goal here is to collect:
- Behavioral data (website analytics, session recordings, heatmaps)
- Survey insights (Net Promoter Score, customer satisfaction surveys)
- Direct customer feedback (interviews, focus groups, online reviews)
- Competitor analysis (how competitors structure their customer journeys)
Combining quantitative and qualitative research provides a complete picture—what customers do, why they do it, and where they struggle.
3. Develop detailed customer personas
Personas should be built from real data, not assumptions. Market researchers use clustering techniques, audience segmentation, and survey insights to group customers into meaningful personas based on:
- Demographics (age, gender, location, job role)
- Behavior (purchasing habits, preferred channels)
- Motivations and pain points
- Decision-making process
A well-defined persona ensures that the journey map is tailored to actual user behavior, making it more actionable.
4. Map out the customer journey stages
Break the journey into clear, sequential stages based on research insights. While the general framework (awareness, consideration, decision, retention, advocacy) applies to most businesses, the specific stages should reflect real-world behavior unique to your business and industry.For example, in B2B SaaS, the journey might include:
- Problem recognition (customer realizes a business challenge)
- Research and comparison (exploring solutions, reading reviews)
- Engagement with sales teams (demos, calls, trials)
- Decision and implementation (finalizing purchase, onboarding process)
- Renewal and advocacy (subscription renewal, referrals, expansion)
Each stage should be based on data, not assumption, ensuring it mirrors the real decision-making process.
5. Identify and analyze touchpoints and channels
Customers interact with brands through multiple touchpoints, often across different devices and platforms. Market research helps uncover which touchpoints matter the most by analyzing:
- Where customers engage (social media, email, search, word-of-mouth)
- Where conversions happen (landing pages, checkout pages, sales calls)
- Where drop-offs occur (abandoned carts, high bounce rates)
A well-researched journey map prioritizes the touchpoints that have the most impact on the customer experience.
6. Assess customer emotions and pain points
Understanding customer sentiment at each stage is critical. Market research techniques like emotion mapping, sentiment analysis, and verbatim feedback analysis reveal where customers feel:
- Confusion (unclear messaging, lack of product information)
- Frustration (technical issues, long wait times, unresponsive support)
- Anxiety (concerns about pricing, hidden fees, long-term commitment)
These insights ensure the journey map reflects not just what happens, but how customers feel throughout the process.
7. Validate the journey map with real customer data
Once the journey map is drafted, it should be tested and validated through:
- Customer interviews to confirm accuracy
- Live user testing to identify friction points
- A/B testing to refine touchpoints
- Ongoing data analysis to keep the map up to date
A journey map is a living document—it should evolve based on new research, emerging trends, and changing customer behaviors.
Utilizing customer journey mapping insights in market research
Creating a customer journey map is just the first step. Its real value comes from applying the insights to improve business strategies, marketing efforts, and customer experience. Market research helps transform a static journey map into a dynamic, data-driven tool for business growth.
Enhancing product development and innovation
Customer journey mapping provides deep insights into how customers interact with products, what challenges they face, and what features they value most. Market researchers analyze feedback from surveys, usability tests, and product analytics to:
- Identify gaps in the product experience—where customers expect certain functionalities but don’t find them.
- Uncover opportunities for new features that address pain points in the journey.
- Pinpoint reasons for product abandonment—whether due to a steep learning curve, performance issues, or lack of personalization.
For example, if journey mapping reveals that many users struggle during onboarding, companies can introduce guided walkthroughs, in-app tooltips, or live chat support to smooth the learning curve.
Improving marketing strategies and campaigns
A data-backed journey map helps marketers:
- Refine messaging at each stage to align with customer motivations.
- Target the right audience with more personalized campaigns.
- Optimize content strategies by identifying what information customers seek before making a decision.
- Reduce drop-offs by addressing friction points in the decision-making process.
For instance, if research shows that customers hesitate due to lack of trust, marketing teams can increase credibility through case studies, testimonials, and industry reports. If customers often compare competitors before purchase, brands can create detailed comparison pages to simplify the decision process.
Optimizing customer service and support
Journey mapping highlights where customers experience frustration and require assistance. Market research helps pinpoint:
- Common support queries and the stage at which they arise.
- Preferred customer service channels (email, chat, phone, self-service).
- Response times that impact customer satisfaction.
By analyzing call transcripts, chatbot interactions, and CSAT (Customer Satisfaction) scores, businesses can proactively address concerns before they escalate. For example, if many users get stuck during checkout, introducing a real-time FAQ widget or proactive chat assistance could significantly reduce cart abandonment.
Identifying opportunities for customer engagement and retention
Retention is just as important as acquisition, and CJM insights reveal:
- What drives long-term loyalty and advocacy among existing customers.
- How to reduce churn by identifying dissatisfaction early.
- The right time and way to introduce loyalty programs, referrals, or upsells.
If journey data shows that customers drop off after their first purchase, businesses can implement post-purchase engagement strategies like:
- Personalized email sequences with educational content.
- Exclusive discounts for repeat buyers.
- Customer feedback loops to address issues before they lead to churn.
For B2B brands, journey mapping can identify the best timing for renewal outreach or account management interventions based on customer behavior patterns.
Challenges and best practices in customer journey mapping
Customer journey mapping can be a powerful tool, but many businesses make critical mistakes that reduce its effectiveness. A well-researched, data-driven journey map helps businesses improve customer experience, but common pitfalls can lead to inaccurate insights and poor strategic decisions.
Here’s how to avoid them and ensure your journey map stays relevant.Many businesses focus only on tracking touchpoints but overlook customer emotions and friction points, which can cause blind spots in their journey mapping efforts.
A well-structured journey map doesn’t just track touchpoints—it highlights pain points, emotional responses, and actionable solutions. The example below illustrates how customers move through different stages, where they experience friction, and how businesses can address their concerns. This kind of structured mapping, when paired with market research, leads to more effective problem-solving
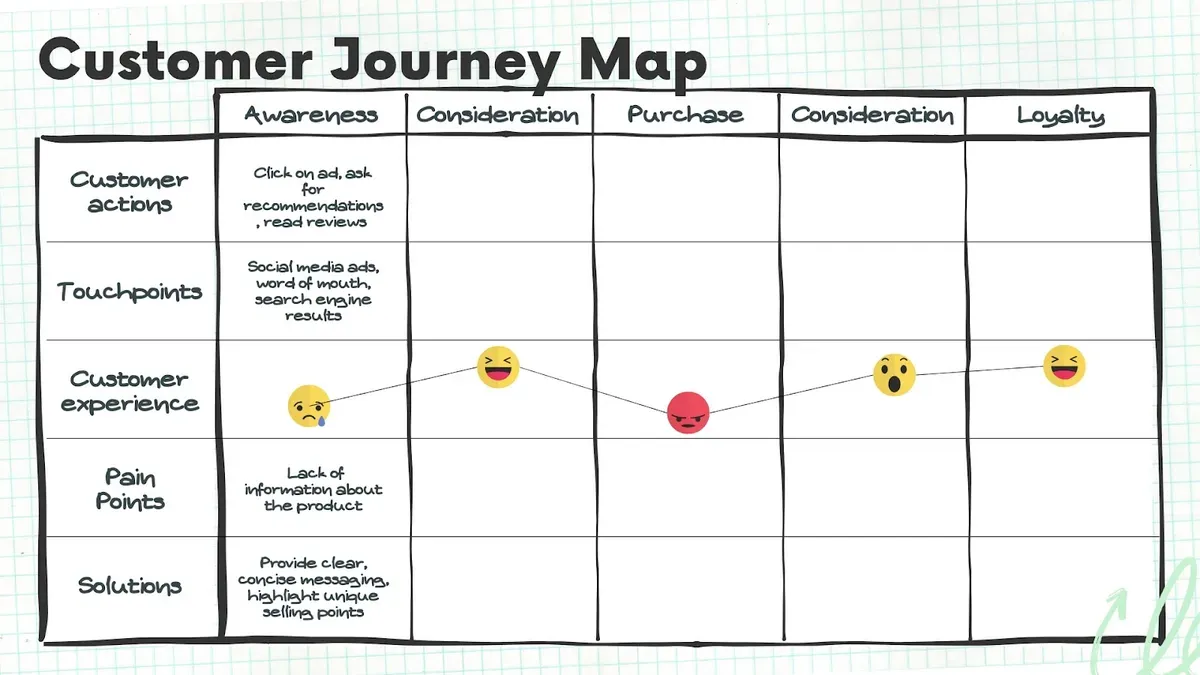
As seen in the customer journey map above, users begin their journey with curiosity and optimism, engaging with ads, recommendations, and reviews. However, as they progress, friction emerges—such as a lack of product information—leading to frustration in the purchase stage. This hesitation often results in drop-offs or delayed decision-making.
Businesses that fail to recognize these emotional shifts may struggle with lower conversion rates and customer dissatisfaction.To prevent these roadblocks, businesses need data-driven insights to understand customer frustrations and refine their journey. Market research helps identify these friction points early, ensuring that messaging, touchpoints, and overall experience align with customer expectations.
Common pitfalls in customer journey mapping and how to avoid them
1. Relying on assumptions instead of real data: One of the biggest mistakes businesses make is creating a hypothetical journey map without validating it with real customer insights. Assumptions about customer behavior can lead to misaligned marketing, sales, and product strategies.How to avoid this:
- Use customer surveys, usability tests, and behavioral analytics to ensure every stage of the journey reflects actual customer behavior.
- Conduct A/B tests and analyze drop-off rates to validate journey pain points.
- Leverage heatmaps, click tracking, and session replays to understand how customers interact with digital touchpoints.
For a more research-driven approach to mapping the customer journey, you can check out this guide on market research methodologies for deeper insights.
2. Focusing only on new customers and ignoring retention: Many journey maps end at the purchase stage, ignoring what happens post-purchase. But retaining customers is just as important as acquiring new ones, especially in industries with high customer acquisition costs.How to avoid this:
- Map out the retention and advocacy stages to understand what keeps customers engaged.
- Analyze customer service interactions and renewal patterns to identify pain points after purchase.
- Use Net Promoter Score (NPS) surveys and customer feedback loops to track satisfaction and loyalty.
For more on how post-purchase experiences influence loyalty, take a look at this article on improving customer experience through journey mapping.
3. Not considering emotional triggers in the journey: A journey map isn’t just about actions—it’s also about how customers feel at different stages. Ignoring customer emotions means missing why they make certain decisions or why they drop off.
How to avoid this:
- Use sentiment analysis and customer feedback to track emotional highs and lows.
- Identify frustration points in self-service tools, checkout processes, or support interactions.
- Implement empathy-driven design in customer experiences to reduce anxiety and improve trust.
4. Creating a static journey map that doesn’t evolve: Customer behaviors, expectations, and technology change over time. A journey map should not be a one-time exercise—it needs to evolve as new insights emerge.
How to avoid this:
- Set a quarterly review process to update the journey map based on new customer data.
- Monitor changing consumer trends, feedback, and emerging customer expectations.
- Use AI-driven analytics to keep journey maps adaptive and relevant.
For a more advanced look at how AI is transforming journey mapping, you can read this guide.
Best practices for effective customer journey mapping
1. Collaborate across teams: A journey map isn’t just for marketing or UX teams. It should involve sales, customer service, product development, and leadership to ensure a holistic view of the customer experience.\
2. Prioritize key customer segments: Not every customer has the same journey. Segmenting journey maps by different customer personas makes the insights more relevant and actionable.
3. Align journey mapping with business goals: Every stage of the journey should tie back to measurable KPIs—whether it’s reducing churn, increasing conversion rates, or improving customer satisfaction.
4. Use visualization tools to make insights actionable: Instead of keeping the journey map in a document, use interactive visualization tools like Miro, Lucidchart, or dedicated CJM platforms to ensure teams can easily access and update it.
Conclusion
Customer journey mapping is more than a visual representation of customer interactions—it’s a strategic tool that, when backed by market research, provides actionable insights for business growth. Without research, journey maps become guesswork, leading to misaligned marketing efforts, product gaps, and customer dissatisfaction.Market research ensures that every stage of the journey is grounded in real customer data, helping businesses:
- Identify touchpoints that matter most through behavioral analytics.
- Understand customer motivations and frustrations using qualitative research.
- Optimize marketing, sales, and customer service strategies with real-time feedback.
- Reduce friction and improve retention by analyzing post-purchase experiences.
A well-researched customer journey map is not a one-time project—it’s an evolving framework that should be continuously updated with fresh insights. As customer behavior, expectations, and technology shift, businesses must adapt their journey maps accordingly.
By integrating qualitative and quantitative research methods, AI-driven analytics, and customer sentiment analysis, market researchers can turn journey mapping into a powerful decision-making tool that improves conversions, loyalty, and overall customer experience.For businesses looking to optimize their customer journey mapping with research-backed insights, leveraging advanced tools and methodologies will ensure better decision-making, reduced friction, and improved customer satisfaction.